In the world of automotive engineering, "Radiator Corrosion Resistance" is crucial. Experts emphasize its significance. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading specialist in corrosion science, states, "Improving radiator durability should be a priority for all manufacturers." Her insights highlight the necessity of addressing corrosion in radiators.
Radiators are vital components in modern vehicles. They help in maintaining optimal engine temperatures. Yet, corrosion remains a common issue. Underlying factors include harsh fluids and environmental conditions. Many manufacturers overlook these challenges, leading to performance issues. The reality is that even slight corrosion can significantly impact engine efficiency.
The industry needs a proactive approach. Developing better materials is one avenue. However, manufacturers must also focus on protective coatings and inhibitors. Effective strategies can enhance radiator longevity. But, the current solutions often fall short. We must reflect on how to truly innovate in "Radiator Corrosion Resistance" for better outcomes.

Radiator corrosion remains a critical issue for many vehicle owners. Understanding its causes is key to preventing damage. According to a 2021 industry report, nearly 30% of radiators show signs of corrosion within five years of use. This deterioration often arises from a combination of electrolysis, coolant breakdown, and environmental factors.
Electrolysis occurs when electrical currents flow through coolant, leading to metal degradation. Many vehicles experience this, especially those with insufficient grounding. Additionally, coolant can lose its effectiveness over time. A study indicated that up to 40% of vehicles ran with degraded coolant. When this happens, the protective properties diminish, allowing corrosion to thrive.
Environmental factors also contribute significantly. High moisture levels and road salt can accelerate corrosion. Many vehicles operated in coastal areas face such challenges. Corrosion not only affects performance; it can lead to costly repairs. It’s important to routinely check coolant quality and vehicle grounding. Addressing these issues early can save money and extend radiator life.
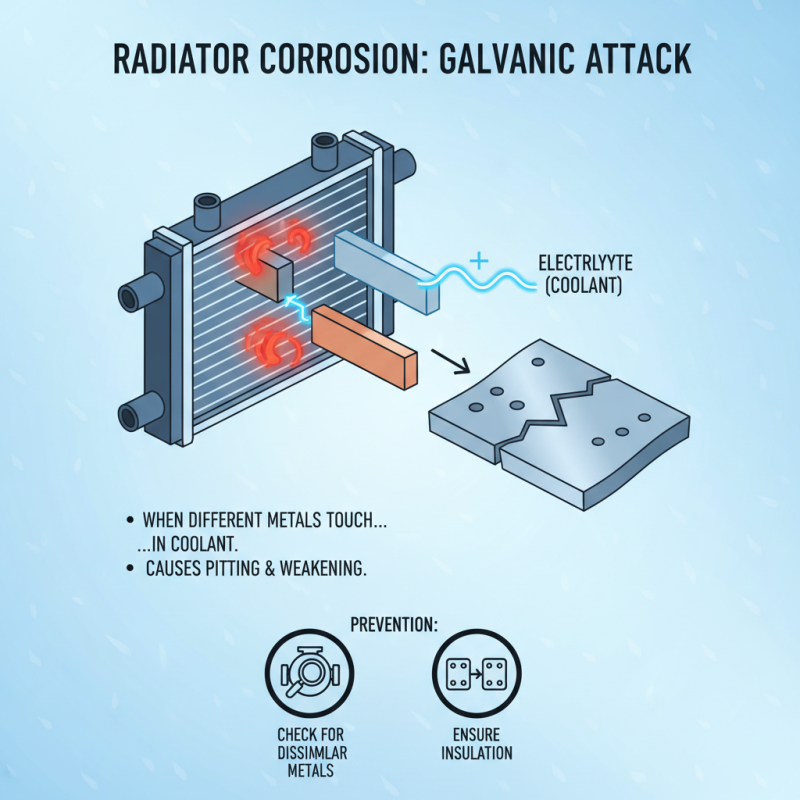
Radiators face various types of corrosion that can significantly impact their performance. One common type is galvanic corrosion. This occurs when two different metals come into contact in the presence of an electrolyte, like coolant. Over time, this reaction can lead to pitting and weakening of the radiator material. It’s essential to regularly check for dissimilar metals in your cooling system and ensure proper insulation between them.
Another type of corrosion is called uniform corrosion. This type occurs evenly across the surface of the radiator. Factors such as poor quality coolant can accelerate this process. Contaminants within the coolant can lead to rust and degradation of metal surfaces. Even if the protection seems effective, one should still inspect the coolant regularly to avoid uniform corrosion.
Lastly, localized corrosion can happen due to imperfections in the radiator finish. Small scratches or damage create weak points. Moisture can settle in these areas, causing rust to develop faster. Taking a moment to review the radiator’s condition after each season can help in catching these issues early. Regular maintenance is crucial for long-term resistance to these corrosion types.
When considering radiator corrosion resistance, choosing the right materials is crucial. Many industry reports emphasize the importance of using aluminum and copper alloys. These materials have shown superior performance in harsh environments. For instance, aluminum can resist oxidation better than steel. Studies indicate that aluminum radiators can extend lifespan by 20% compared to traditional materials.
Coatings also play a significant role in enhancing corrosion resistance. Polymer coatings are particularly effective. They create a barrier that protects against moisture and chemicals. Research shows that a well-applied polymer coating can reduce corrosion rates by up to 90%. However, the application process can often be inconsistent. This inconsistency can lead to weak spots, highlighting the need for careful inspection.
Additionally, surface treatments like anodizing further improve corrosion resistance. This process increases surface hardness and creates a protective oxide layer. Yet, not all anodized surfaces are created equal. Variability in the anodizing process can affect durability. Continuous improvement and quality control are essential to maximize the effectiveness of these coatings. Testing and adapting processes based on performance feedback can lead to better outcomes in the long run.
Routine maintenance is critical for preventing radiator corrosion. Regularly check the coolant levels. Low coolant can cause overheating and corrosion. Use distilled water when filling. It’s less likely to introduce minerals that can cause buildup. Inspect hoses and connections for leaks. Even small leaks can lead to significant damage over time.
Consider using a coolant additive specifically designed for corrosion protection. These additives create a protective layer on metal surfaces. They can help extend the life of the radiator. Don’t ignore the importance of flushing the cooling system. This process removes debris and prevents corrosion. It’s best done every few years.
Pay attention to the external condition of the radiator too. Dirt and debris can trap moisture, leading to rust. Regularly clean the exterior. Look for signs of wear or physical damage. A single dent can compromise the unit’s integrity, allowing corrosion to take hold. Reflection on these habits can guide more effective maintenance. Each step matters in ensuring a longer lifespan for your radiator.
| Maintenance Practice | Frequency | Effectiveness (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Cleaning | Monthly | 85% | Reduces buildup of corrosive substances. |
| Coolant Replacement | Every 2 years | 90% | Prevents coolant degradation that leads to corrosion. |
| Inspect for Leaks | Quarterly | 80% | Early detection prevents further damage. |
| Check pH Levels | Twice a year | 75% | Maintains optimal coolant conditions. |
| Apply Anti-Corrosion Coating | Every 5 years | 95% | Provides an additional barrier against corrosion. |
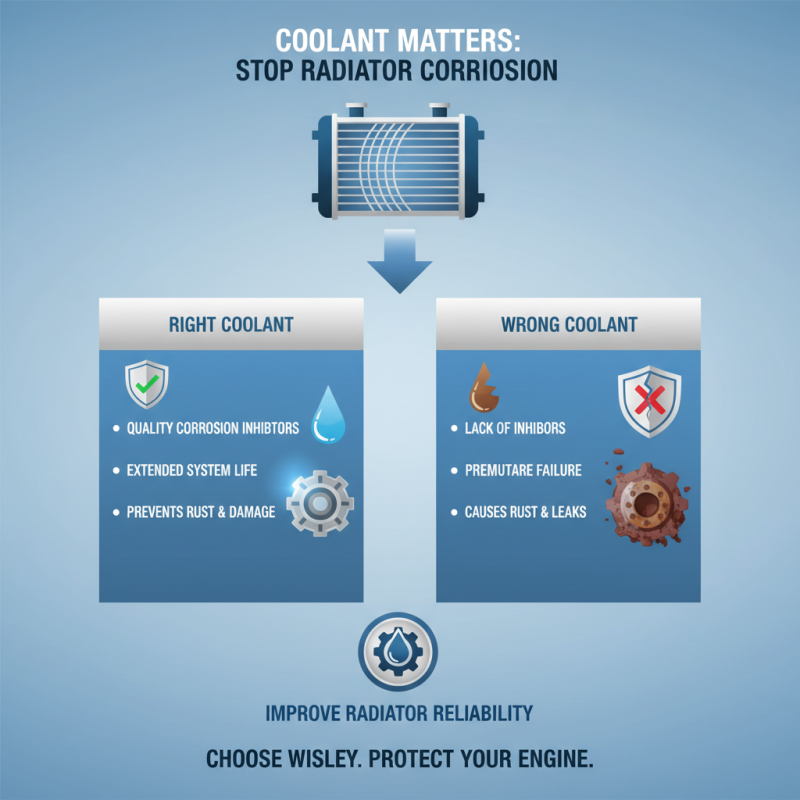
Choosing the right coolant is crucial for improving radiator corrosion resistance. Numerous factors influence coolant performance. One mistake is using a low-quality coolant that lacks proper corrosion inhibitors. This can lead to rust and damage over time.
Regularly check coolant levels and quality. If the coolant appears rusty or discolored, it’s time to replace it. Consider a coolant specifically designed to protect metals commonly found in radiators. Look for options with phosphates or silicates. These additives help prevent corrosion.
Tips: Always read coolant labels for compatibility with your vehicle. Mixing different coolants can cause gelling and reduce effectiveness. Don’t overlook the importance of regular maintenance. Flushing your radiator every couple of years can eliminate debris and old coolant. This step is often neglected but vital for long-term protection.