In the realm of thermal management and energy transfer, **Heat Exchanger Tubes** play a crucial role across various industries. These specialized tubes are designed to facilitate efficient heat exchange between two or more fluids, making them pivotal in applications ranging from power generation to chemical processing. Understanding the different types of heat exchanger tubes available and their specific applications is essential for engineers and maintenance professionals. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right type of tube for a specific application but also contributes to optimizing performance and longevity.
Moreover, routine maintenance and proper operational practices are critical to ensuring the efficiency and reliability of heat exchangers. By implementing effective maintenance tips, organizations can prevent common issues such as fouling, corrosion, and pressure drops that can compromise system performance. This essential guide aims to provide an overview of various heat exchanger tube types, their respective applications, and invaluable maintenance strategies to enhance operational efficiency and extend the lifespan of these vital components. Through a comprehensive understanding of these elements, professionals can ensure optimal thermal performance and reduced operational costs across industrial processes.
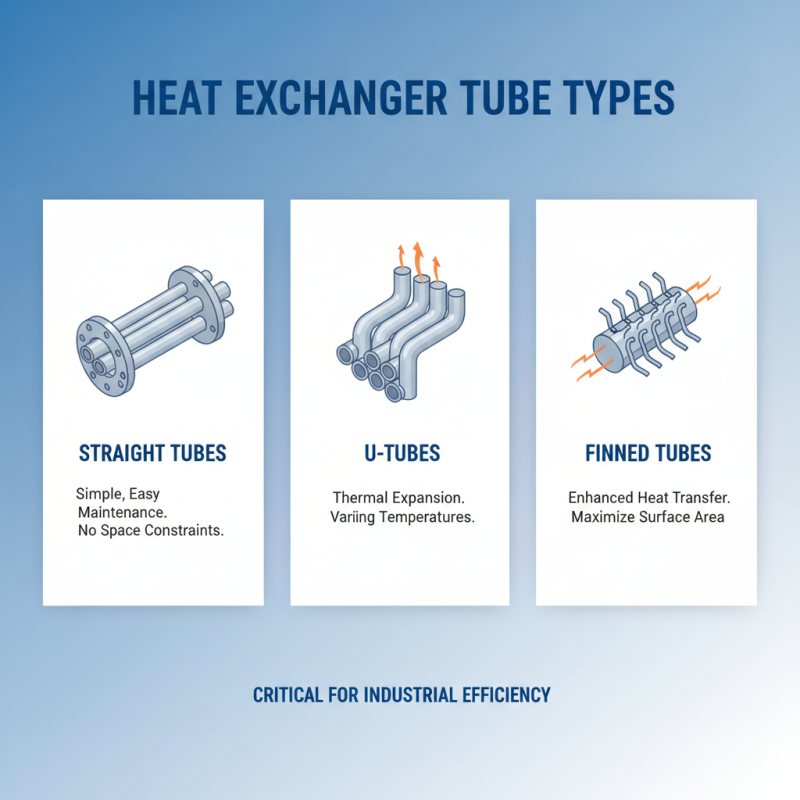
Heat exchangers are critical components in various industrial processes, and the types of tubes used in these systems significantly influence their efficiency and effectiveness. The most common types of heat exchanger tubes include straight tubes, U-tubes, and finned tubes, each with unique characteristics suited for different applications. Straight tubes, known for their simplicity and ease of maintenance, are widely utilized in applications where space is not a constraint. Conversely, U-tubes are ideal for systems requiring thermal expansion accommodation, often used in environments with varying temperatures. Finned tubes are designed to enhance heat transfer capabilities, making them suitable for air-cooled exchangers and applications where maximizing surface area is crucial.
According to a report by the Global Heat Exchanger Market, the demand for specialized heat exchanger tubes has increased by 4.5% annually, reflecting the growing need for efficiency in sectors such as chemical processing, power generation, and HVAC. The choice of tube material also plays an essential role, with options like stainless steel, copper, and titanium being favored for their resistance to corrosion and high-temperature performance. In applications such as petrochemical facilities, the right tube type can lead to a 20% increase in thermal efficiency, underscoring the importance of selecting the appropriate tube design based on specific operational requirements and environmental conditions. Proper maintenance practices, including regular inspections and cleaning, further enhance the lifespan and performance of these critical heat exchanger components.
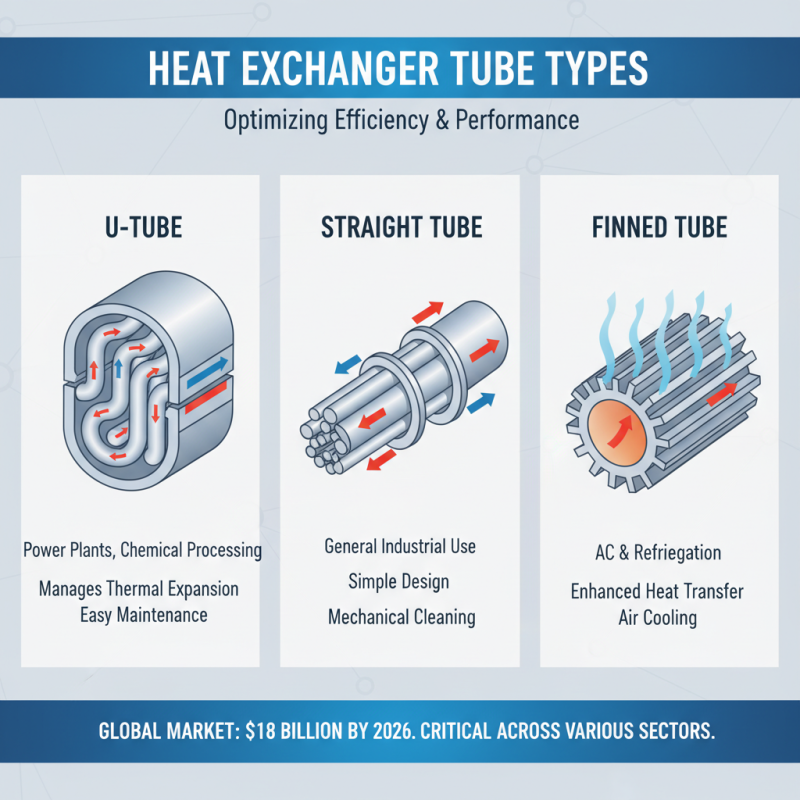
Heat exchangers play a critical role in various industrial processes, with tube types designed for specific applications that optimize both efficiency and performance. Common tube types include U-tube, straight tube, and finned tube designs, each tailored for specific settings. For instance, U-tube heat exchangers are often employed in power plants and chemical processing due to their ability to handle thermal expansion and facilitate easy maintenance. Meanwhile, finned tube heat exchangers are predominantly used in air conditioning systems and refrigeration – their extended surface area allows for enhanced heat transfer efficiency, making them ideal for cooling applications. Industry reports suggest that the market for heat exchangers is projected to reach $18 billion by 2026, underscoring their importance across various sectors.
When considering heat exchanger tubes for new projects or upgrades, it's essential to evaluate their maintenance requirements and operational efficiency. One critical tip is to conduct regular inspections for scale buildup and corrosion, which can significantly impede performance and efficiency. Utilizing advanced materials, such as copper-nickel alloys, can also prolong service life, especially in seawater applications. Additionally, if operating in environments prone to fouling, implementing a cleaning schedule can prevent performance degradation and extend operational longevity, ensuring that the system continues to perform at optimal levels.
Ultimately, awareness of the specific applications of different tube types and their maintenance necessities is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of heat exchangers in various industrial applications.
When managing the performance and longevity of heat exchanger tubes, implementing critical maintenance practices is essential. Regular inspections are vital for identifying potential issues, such as corrosion or fouling, which can significantly impact efficiency. According to the Chemical Engineering Magazine, up to 50% of heat exchanger failures can be attributed to inadequate maintenance, highlighting the importance of a proactive maintenance schedule.
Routine cleaning is one of the most effective ways to enhance heat exchanger performance. The National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE) states that effective cleaning methods can improve heat transfer rates by as much as 30%. Different cleaning techniques, such as chemical cleaning and mechanical cleaning, should be employed based on the type of fouling and tube material. Additionally, monitoring operational parameters closely—such as temperature differential and flow rate—can help in identifying signs of wear or blockage before they escalate into serious problems.
Replacing worn-out or damaged tubes in a timely manner is also crucial. Utilizing predictive maintenance software can help in forecasting tube failure based on historical performance data and current operating conditions. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), implementing an effective maintenance strategy can result in life extension of heat exchanger tubes by up to 40%, which significantly reduces replacement costs and downtime in industrial operations.
When selecting heat exchanger tubes, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. One of the primary considerations is the material of the tubes, which should be chosen based on the working environment and the fluids being exchanged. For instance, corrosion resistance is critical in applications involving aggressive chemicals or harsh conditions, while thermal conductivity is essential for maximizing heat transfer efficiency. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and various alloys, each offering distinct performance characteristics suited to particular applications.
Another significant factor influencing tube selection is the design and geometry of the heat exchanger. The intended operating pressure and temperature can determine whether a straight or finned tube configuration is more suitable. Finned tubes increase surface area and enhance heat transfer in air-cooled applications, while straight tubes may be preferred for liquid-to-liquid exchanges. Additionally, the required flow rate and potential fouling issues should guide the choice of tube size and type, as these can affect maintenance schedules and overall system efficiency. By carefully considering these factors, engineers can select the most effective heat exchanger tubes for their specific applications.
| Tube Type | Material | Application | Maintenance Tips | Factors for Selection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight Tubes | Stainless Steel | Oil Refining | Regular inspection for corrosion | Cost, Flow type |
| U-Tubes | Titanium | Chemical Processing | Check for blockages | Temperature, Pressure |
| Coiled Tubes | Copper | HVAC Systems | Keep free from debris | Space, Design |
| Fin Tubes | Aluminum | Refrigeration | Inspect fins for bends | Efficiency, Airflow |
| Spiral Tubes | Carbon Steel | Waste Heat Recovery | Monitor for leaks | Fluid properties, Installation constraints |
Heat exchangers are crucial components in various industrial applications, enabling efficient heat transfer while maintaining operational efficiency. However, they are not immune to problems that can hinder performance. Common issues encountered in heat exchanger tubes include corrosion, fouling, and leaks. According to a report by the Heat Exchange Institute, improper maintenance can lead to up to a 30% loss in thermal efficiency, highlighting the importance of addressing these issues promptly.
Corrosion is often a result of improper material selection or inadequate protective measures. To mitigate this, operators should regularly inspect and maintain tube integrity, particularly in environments with aggressive fluids. Fouling, on the other hand, can occur due to the accumulation of sediment and deposits on tube surfaces, which can decrease heat transfer efficiency by as much as 50%. Implementing a routine cleaning schedule utilizing methods such as mechanical brushing or chemical cleaning can alleviate fouling-related problems.
Finally, leaks in the heat exchanger tubes not only compromise system performance but can also lead to environmental concerns. Proper testing techniques, such as pressure testing and ultrasonic testing, should be employed to detect leaks early. Maintaining a detailed log of operational conditions and conducting regular inspections can help identify potential deterioration before they escalate into significant failures, thus prolonging the lifespan of the heat exchangers and ensuring operational reliability.