Choosing the right Heat Exchanger Tube is crucial in various industries. Heat exchangers are vital for processes that require efficient thermal management. According to a 2022 report by the Global Heat Exchanger Market Analysis, the demand for heat exchangers is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, projected to reach $18 billion by 2026.
Industry expert Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned thermal systems engineer, states, "Selecting the appropriate tube material can enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs." Different applications require specific characteristics in a Heat Exchanger Tube. Factors such as corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and pressure ratings play critical roles.
Choosing a tube that does not match application needs could lead to failures. Many companies overlook these factors and face costly downtimes. Thus, understanding the application’s requirements is essential for success. Carefully evaluating material types and configurations is necessary for optimal performance. Selecting the right Heat Exchanger Tube demands attention and expertise.

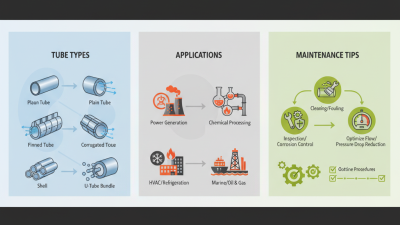
Heat exchangers play a vital role in various industries. Selecting the right tube enhances efficiency and performance. There are several types of heat exchanger tubes: one can choose between shell and tube, plate, or air-cooled designs. Each has its distinct advantages. For example, the shell and tube type is often preferred for its high heat transfer efficiency.
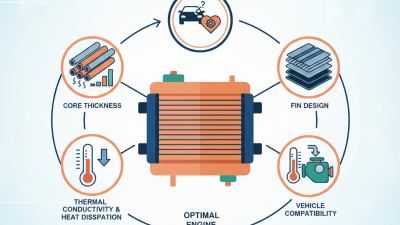
Understanding the specifications of heat exchanger tubes is crucial. Factors such as diameter, material, and wall thickness contribute to operational performance. Carbon steel is popular due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. Nevertheless, it may not be suitable for all fluids. A recent report highlighted that 30% of failures in heat exchangers are linked to corrosion issues. Reflecting on material choices can lead to better longevity.
The size of the heat exchanger tube impacts its overall performance. Larger tubes may promote higher flow rates but can result in pressure drops. Studies indicate that a 10% increase in diameter can reduce pressure drops by 15%. However, some designs may not accommodate larger sizes, leading to inefficiencies. Choosing the right balance is essential for maximizing function. Each application you'll face has unique requirements.
This chart illustrates the heat transfer efficiency and corrosion resistance of different heat exchanger tube materials commonly used in various applications.
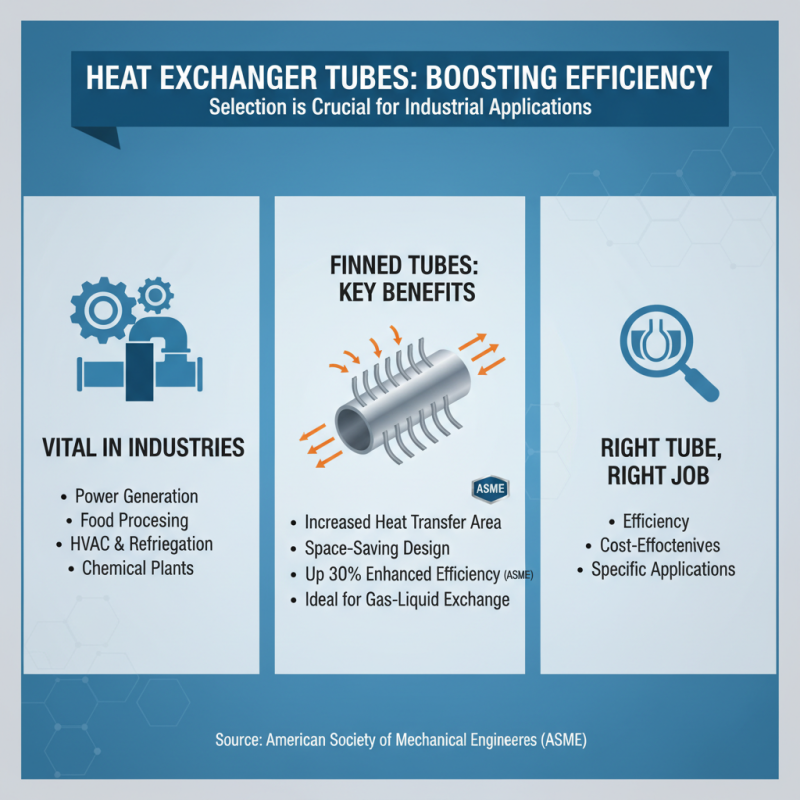
Heat exchangers are vital in numerous industries, from power generation to food processing. Selecting the right heat exchanger tube is crucial for efficiency. Various types of tubes cater to specific applications. For example, finned tubes increase heat transfer area. They are useful in environments where space is limited. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, finned tubes can enhance heat transfer by up to 30%.
On the other hand, seamless tubes have distinct advantages in high-pressure applications. They are often preferred in oil and gas sectors. These tubes resist corrosion and can handle significant stress. However, they may cost more than other options. In fact, a report by the International Energy Agency indicates that seamless tubes constitute 60% of the total heat exchanger tube market in those industries.
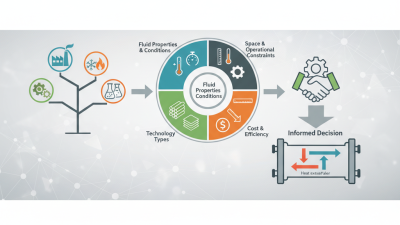
Copper and stainless steel are common materials for these tubes. Copper provides excellent thermal conductivity but is susceptible to corrosion. Stainless steel offers durability and high resistance to corrosion. However, it may not transfer heat as efficiently as copper. This trade-off needs careful consideration. Industry professionals must evaluate operational parameters and installation settings to make informed decisions. The complexity of this selection process often raises questions. For this reason, detailed knowledge and reliable data are essential to achieving the right choice.
When selecting heat exchanger tubes, various factors can impact performance. Material choice plays a crucial role.
Stainless steel is common due to its corrosion resistance. However,
copper-nickel alloys excel in marine applications, as reports indicate they withstand seawater corrosiveness better.
Another important factor is tube diameter. Larger diameters allow higher flow rates. A study from the Heat Transfer Research Institute indicates that increasing diameter by just 10% can improve heat transfer efficiency by up to 15%. However, larger tubes may complicate installation and maintenance, which can be costly.
Consider the system’s operating temperatures. High temperatures often demand special alloys to avoid warping or failure. A mismatch can lead to catastrophic failures, draining resources. The right heat exchanger tube can save energy and reduce downtime. Yet, engineers must carefully analyze their unique conditions to make informed choices.
When choosing materials for heat exchanger tubes, various options present both advantages and disadvantages. Stainless steel, for example, offers durability and corrosion resistance. However, it can be costly and may not perform well in extreme temperatures. This makes it essential to weigh the benefits against the potential downsides.
Copper is another popular choice. It excels in thermal conductivity, allowing efficient heat transfer. Yet, it is susceptible to corrosion in certain environments. This factor can lead to premature failure, which is a significant risk for many applications. Careful consideration is essential when deciding on copper.
Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant. It's an excellent choice for certain mobile applications. Yet, its lower strength can be a drawback in demanding conditions. Finding the perfect balance between cost, efficiency, and longevity can be challenging. Each material comes with its considerations. Evaluation must be thorough, factoring in the specific requirements of your heat exchanger application.
| Material | Pros | Cons | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, high strength, durable | Higher cost, can suffer from stress corrosion cracking | Food processing, chemical industries |
| Copper | Excellent thermal conductivity, antimicrobial properties | Corrosion prone in certain environments, expensive | Residential HVAC systems, refrigeration |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, good thermal conductivity, low cost | Lower corrosion resistance, less durable | Air conditioning units, automotive radiators |
| Titanium | Exceptional corrosion resistance, strong | Very high cost, difficult to fabricate | Marine applications, chemical processing |
| Carbon Steel | Low cost, good mechanical properties | Prone to rust and corrosion, limited temperature range | Power generation, oil and gas |
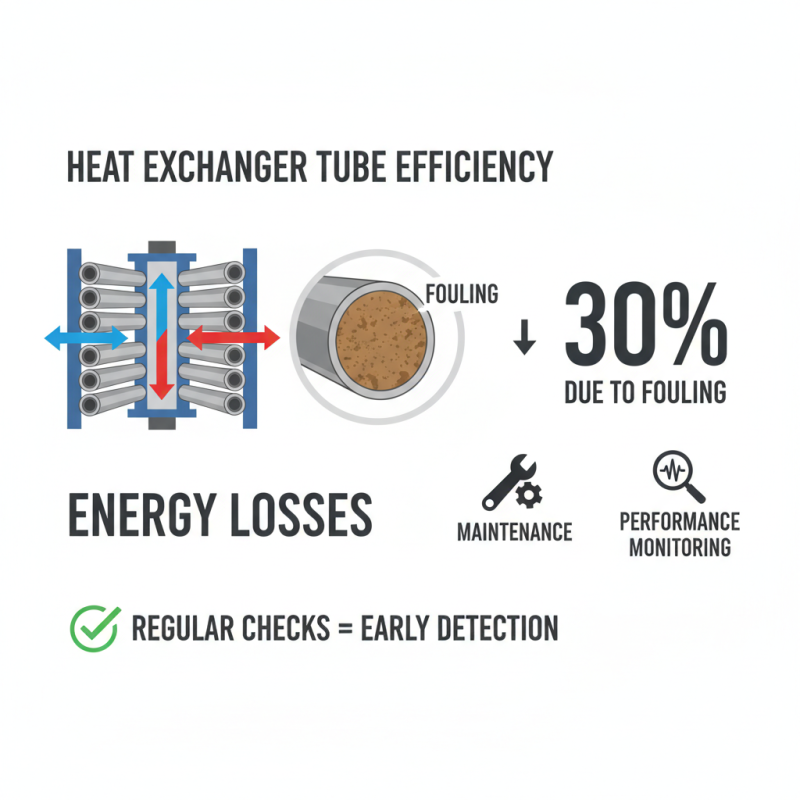
Heat exchanger tubes are crucial in various industries. Maintenance and performance monitoring are vital to ensure efficiency. Studies show that 30% of energy losses in heat exchangers come from fouling in the tubes. Regular checks can help detect these issues early.
Tips: Implement a regular inspection schedule. Look for signs of corrosion or deposits. These can impair heat transfer efficiency.
Performance can be impacted by many factors. Tube materials, design, and flow rates all play a role. Using the wrong tube can lead to decreased effectiveness. A report indicated that improper maintenance can increase operational costs by up to 20%. It’s essential to choose the right tube and care for it properly.
Tips: Consider thermal expansion when selecting tubes. Frequent misalignment can lead to leaks. Monitor changes in pressure as they can signal underlying problems.