As industries continue to evolve, the demand for efficient temperature regulation systems has never been higher. The market for Thermal Management Coolers is projected to grow significantly, with a report from ResearchAndMarkets stating that the global thermal management market is expected to reach $24 billion by 2025. This underscores the critical role these systems play in enhancing performance and extending the lifespan of electronic components, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
According to Dr. Emily Rogers, a leading expert in thermal solutions, “Choosing the right Thermal Management Cooler is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and ensuring reliability in high-performance applications.” This assertion highlights the importance of selecting appropriate cooling technologies tailored to specific operational needs. As companies strive to optimize their products, understanding the various cooling solutions available—ranging from passive to active systems—becomes crucial for ensuring both efficiency and sustainability.
In light of this growing industry and the rising significance of effective thermal management, it is vital for businesses to stay informed on the latest advancements and trends in cooler technologies. The year 2025 presents an opportunity to reassess and innovate approaches to thermal management, making educated decisions to enhance both product performance and energy efficiency.


Effective thermal management is crucial in a variety of industries, from electronics to manufacturing, as it directly impacts performance, reliability, and safety. According to a report by the International Thermal Management Association, overheating can reduce the lifespan of electronics by up to 50% and significantly impair their functionality. As devices and equipment become more compact and powerful, the need for efficient thermal solutions becomes increasingly important. Proper thermal management helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing damage and ensuring consistent performance.
When selecting a thermal management cooler, it's essential to consider the specific thermal requirements of your applications. Different environments and operational conditions call for diverse cooling solutions, ranging from passive to active systems. A recent study indicated that passive cooling solutions are often preferred in scenarios where noise reduction is a priority, while active systems are favored in high-density applications where excessive heat build-up is a concern.
**Tips**: Always assess the thermal load and space constraints before making a decision. Additionally, look for coolers designed with advanced materials, as they often offer enhanced thermal conductivity and efficiency. Regular maintenance of your cooling system is also crucial—any buildup of dust or debris can significantly hinder performance and lead to overheating.
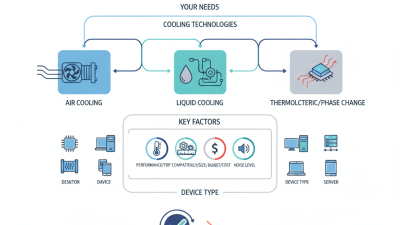
When selecting a thermal management cooler, it's important to understand the various types available, as each serves different needs and applications. The most common types include air coolers, liquid coolers, and phase change coolers. Air coolers work by dissipating heat through air convection and are typically the most cost-effective option, making them ideal for standard computing tasks. They are usually quieter and easier to install, making them a popular choice for home users and budget-conscious consumers.
On the other hand, liquid coolers provide superior heat dissipation, making them suitable for high-performance computing, such as gaming or professional applications. These systems circulate liquid through a cooling block that absorbs heat and transfers it to a radiator, where the heat is released into the air. While slightly more complex to install and maintain, their efficiency and cooling performance are highly valued by enthusiasts and professionals.
Lastly, phase change coolers operate similarly to refrigeration systems, allowing for extreme temperature control. These coolers use a refrigerant that changes from liquid to gas, absorbing heat in the process. Typically used in specialized applications requiring low temperatures, phase change coolers can effectively manage thermal loads that exceed the typical capabilities of air or liquid cooling.
Understanding these types will help you make an informed decision when selecting a cooler that best fits your thermal management needs.
When selecting a thermal management cooler, several key features should be considered to ensure optimal performance tailored to your specific needs. First and foremost, the cooling capacity is crucial; it defines how effective a cooler will be in dissipating heat. Look for coolers with adjustable performance settings or those designed for varying thermal loads. Additionally, assess the size and compatibility of the cooler with your existing systems. A cooler that fits well not only ensures efficient heat management but also helps maintain airflow within the system.
Another important factor is the noise level produced by the cooler during operation. For environments where noise can be a distraction, such as offices or during night-time use, a quieter cooler is essential. Furthermore, examine the construction materials and design; durable materials can enhance the cooler's lifespan and efficiency. Finally, consider ease of maintenance, as coolers that require frequent cleaning or complex maintenance routines can become cumbersome over time. By prioritizing these features, users can find a thermal management solution that meets their specific requirements effectively.
| Feature | Description | Importance | Recommended Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling Capacity | Measured in Watts, indicates how much heat the cooler can dissipate. | High importance for performance. | 100W - 300W depending on application |
| Noise Level | Measured in dB, it's important for quiet environments. | Medium importance based on usage. | Below 30 dB for quiet use |
| Size and Form Factor | Dimensions that fit your equipment seamlessly. | High importance for compatibility. | Compact designs preferred |
| Power Consumption | How much energy the cooler uses when operating. | Medium importance, affects operating costs. | Under 50W |
| Material Quality | Durability and thermal conductivity of the materials used. | High importance for longevity. | Aluminum or copper preferred |
When evaluating thermal management coolers, it's essential to consider several performance metrics to ensure the chosen solution meets your specific needs. The first key metric is thermal performance, which includes the cooler’s ability to dissipate heat efficiently under load. This is often quantified by its thermal resistance, expressed in degrees Celsius per watt. A lower thermal resistance indicates better performance, allowing for more effective heat transfer from the targeted component to the cooler.
Another critical performance metric is airflow rate, typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). This metric is vital for understanding how effectively a cooler can move air across its heat exchange surfaces. Higher airflow rates often enhance cooling efficiency, particularly in environments with higher ambient temperatures or when dealing with high-performance components that generate significant heat. Additionally, noise levels, measured in decibels (dB), should also be taken into account, especially in settings where noise can be a distraction. Balancing thermal performance, airflow, and noise levels will help you choose a thermal management cooler that fits your requirements effectively.
Maintaining and extending the life of your thermal management cooler involves a few essential practices that ensure optimal performance. First, regular cleaning is crucial. Dust and debris can accumulate in the fins and fans of the cooler, hindering airflow and cooling efficiency. It’s advisable to use compressed air to blow out any buildup carefully. Additionally, ensure that the cooler is placed in a well-ventilated area, avoiding restricted spaces that can trap heat and diminish performance.
Another significant aspect of cooler maintenance is monitoring the temperature and performance regularly. Keeping an eye on temperature readings can help you detect early signs of inefficiency. If you notice that temperatures are creeping higher than typical levels, inspect the cooler for any signs of wear or malfunction. Lastly, consider inspecting and replacing thermal paste if applicable; this can improve heat transfer between the cooler and the component it serves, ultimately enhancing longevity and reliability. By adhering to these maintenance tips, you can ensure your cooler operates efficiently for an extended period, safeguarding your equipment from potential overheating issues.