In today's fast-paced technological landscape, effective thermal management has become a critical factor in the performance and longevity of electronic devices. A well-designed Thermal Management Cooler plays a vital role in dissipating heat generated by various components, ensuring that systems operate within their optimum thermal ranges. With various cooling solutions available, selecting the best one tailored to your specific needs can seem overwhelming.
This guide aims to simplify the decision-making process by outlining essential factors to consider when choosing a Thermal Management Cooler. From understanding the different cooling technologies to assessing compatibility with your device, we will explore the key elements that influence the effectiveness and efficiency of cooling solutions. By the end of this article, readers will be equipped with the knowledge needed to make informed choices, optimizing their systems for enhanced performance and durability.
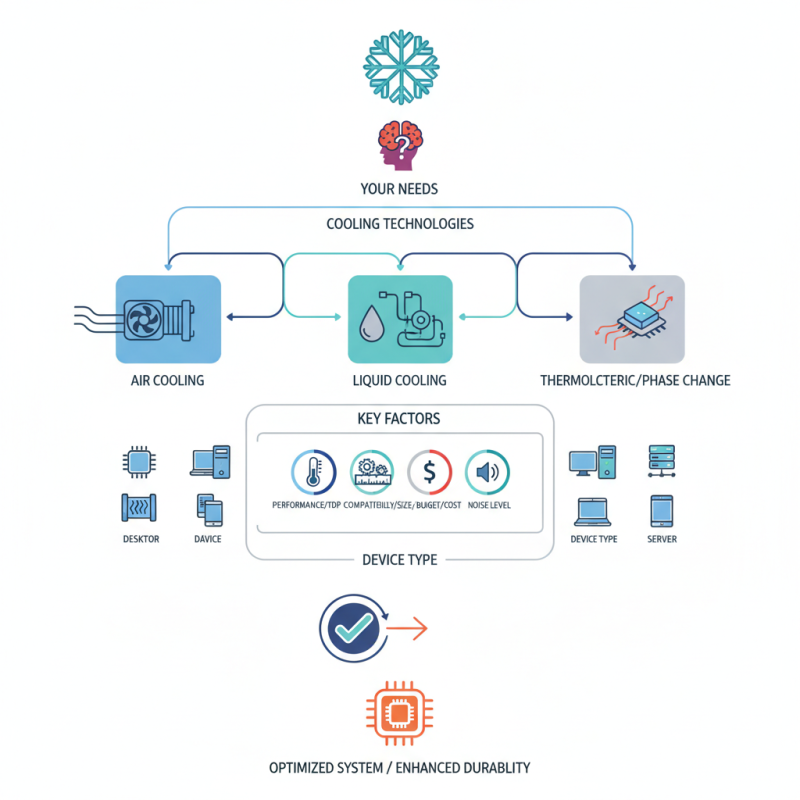
When selecting the best thermal management cooler for your needs, several key considerations should guide your decision-making process. First and foremost, assess the thermal requirements of your specific application. Understanding the maximum heat load generated by your equipment will help you choose a cooler that can adequately dissipate heat to maintain optimal performance. Additionally, consider the environmental conditions in which the cooler will operate, such as ambient temperature and humidity, as these factors can significantly impact cooling efficiency.
Another crucial aspect to evaluate is the design and size of the cooler. Ensure that it fits not just within your spatial constraints but also complements the overall system layout. Look for features such as airflow design, material durability, and ease of maintenance. Finally, think about the noise level produced by the cooler. Depending on where it will be installed, low-noise operation may be essential, especially in environments that require minimal disruption. By taking these considerations into account, you can select a thermal management cooler that meets your specific needs and enhances the performance of your equipment.
This chart compares the temperature reduction capabilities of various thermal management coolers, aiding in the decision-making process for selecting the best cooler for your specific needs.
When selecting the best thermal management cooler, it's crucial to understand the various types available in the market. The most common types of coolers include passive, active, and thermoelectric coolers. Passive coolers rely on natural convection, dissipating heat without additional energy, making them energy-efficient options for applications with moderate thermal output. In contrast, active coolers use fans or pumps to enhance airflow, allowing for better heat dissipation, which is ideal for high-performance computing environments. Thermoelectric coolers, known for their compact size and reliability, utilize the Peltier effect to transfer heat, providing precise temperature control and often used in sensitive electronic devices.
When evaluating thermal management solutions, consider your specific needs. For instance, the 2022 Thermal Management Report indicates that systems requiring a thermal resistance of less than 1°C/W benefit significantly from active cooling solutions. Meanwhile, passive coolers can be used effectively in lower-density applications, as they present minimal noise pollution and reduced maintenance costs.
Tips: Always account for the ambient temperature and the total heat output from the components to determine the necessary cooling capacity. Additionally, inspect the cooler's airflow design, as this can significantly impact thermal performance and efficiency. Using simulation tools can help visualize thermal dynamics in your setup before making a purchase, ensuring you select the optimal solution for your environment.

When selecting a thermal management cooler, understanding thermal performance metrics is crucial. Two of the most significant metrics are BTU ratings and efficiency levels. BTU, or British Thermal Unit, measures the rate at which heat is removed or released by the cooler. A higher BTU rating indicates that the cooler can handle more heat, which is essential for environments with high thermal loads. Understanding your specific requirements based on the equipment and ambient conditions will guide your selection process. For instance, if you're managing high-performance computing systems, opt for coolers with elevated BTU ratings to ensure adequate thermal control and stability.
Equally important is the efficiency level of the cooler, which reflects how effectively the unit converts input energy into cooling power. Efficiency can significantly impact operating costs and energy consumption. When choosing a cooler, consider systems with high efficiency ratings, as they not only minimize energy wastage but also provide more reliable thermal management over extended periods. Evaluating both BTU ratings and efficiency levels will lead you to a thermal management solution that not only meets your needs but also promotes sustainability in your operations.
When selecting a thermal management cooler, it is crucial to assess compatibility with your existing systems, focusing on size, fit, and integration. According to recent industry reports, nearly 45% of failed thermal management implementations are attributed to poor compatibility with equipment dimensions and layouts. Thus, measuring the available space in your system should be the first step. Ensure that the cooler you choose fits within the designated area without obstructing airflow or other components. Consider both the physical dimensions and the mounting orientations that may be required for optimal performance.
Another essential factor in compatibility assessment lies in the integration with existing systems. A cooler must be compatible not just on a physical level but also in terms of thermal performance needs. Specifically, it is important to ensure that the cooler provides sufficient cooling capacity to manage the heat dissipation requirements of your application. Recent studies indicate that applications with inadequate cooling may experience efficiency drops of up to 20%, underscoring the importance of a correctly integrated thermal management solution.
Tips: Always consult component specifications and user manuals before making a purchase. A compatibility checklist can be invaluable in preventing costly missteps. Additionally, consider simulation tools that model the thermal dynamics of your existing systems, as this can provide insights into necessary adjustments for effective cooler integration.
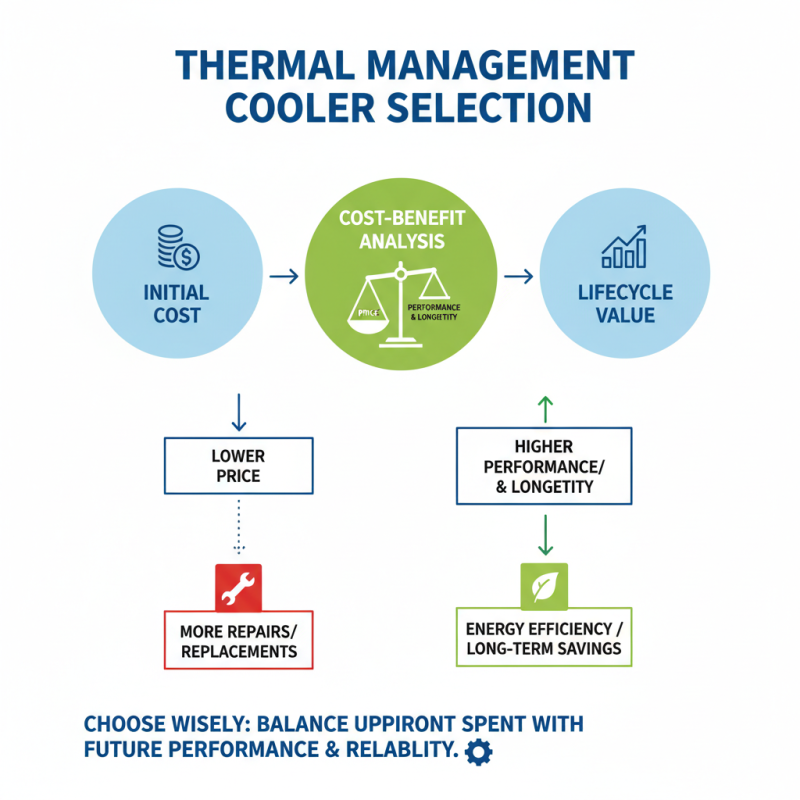
When selecting a thermal management cooler, it’s essential to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis that weighs price against performance and longevity. The initial purchase cost is just one part of the equation; the performance level of the cooler must align with the specific cooling requirements of your application. A higher-priced cooler with advanced technology may deliver superior efficiency and a longer lifespan, ultimately justifying its expense. Therefore, evaluating the energy consumption and cooling capacity in relation to your specific needs can provide insight into whether a lower-cost option may lead to more extensive replacements or repairs in the future.
Longevity is another critical factor in this analysis. A cooler designed with higher-quality materials and construction will likely last longer, resulting in less frequent replacements and maintenance costs. In contrast, a cheaper, less durable solution might save money upfront but could incur higher costs over time due to its inefficiency and the need for eventual replacement. A comprehensive evaluation should not only account for the immediate financial outlay but also consider the operational costs and durability over the cooler’s lifespan, allowing for a more informed decision that aligns with both your budget and cooling requirements.