The efficiency and longevity of modern engines are heavily reliant on effective thermal management systems. Among these systems, the "Air Cooled Oil Cooler" stands out as a crucial component in maintaining optimal oil temperatures, thereby ensuring peak performance and reliability. According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), overheating of engine oil can lead to significant degradation in performance, with studies indicating that for every 10 degrees Celsius increase in oil temperature, the oil's lifespan can be reduced by approximately 50%. This highlights the critical need for robust cooling solutions.
An Air Cooled Oil Cooler operates by dissipating heat from the engine oil directly to the surrounding air, using a series of fins and airflow mechanisms to enhance heat exchange efficiency. This type of cooler is particularly advantageous in environments where traditional water-cooled systems may struggle, offering a weight-efficient and low-maintenance alternative. According to industry projections, the market for oil cooling systems, including air-cooled variants, is expected to grow significantly, driven by increasing demands for high-performance engines and stringent emissions regulations.
As automotive technology continues to advance, understanding the function and benefits of Air Cooled Oil Coolers becomes increasingly vital for manufacturers and consumers alike. By optimizing oil temperature, these coolers not only improve engine efficiency but also contribute to better fuel economy and reduced emissions, making them an integral part of the engineering conversation around modern vehicle design.
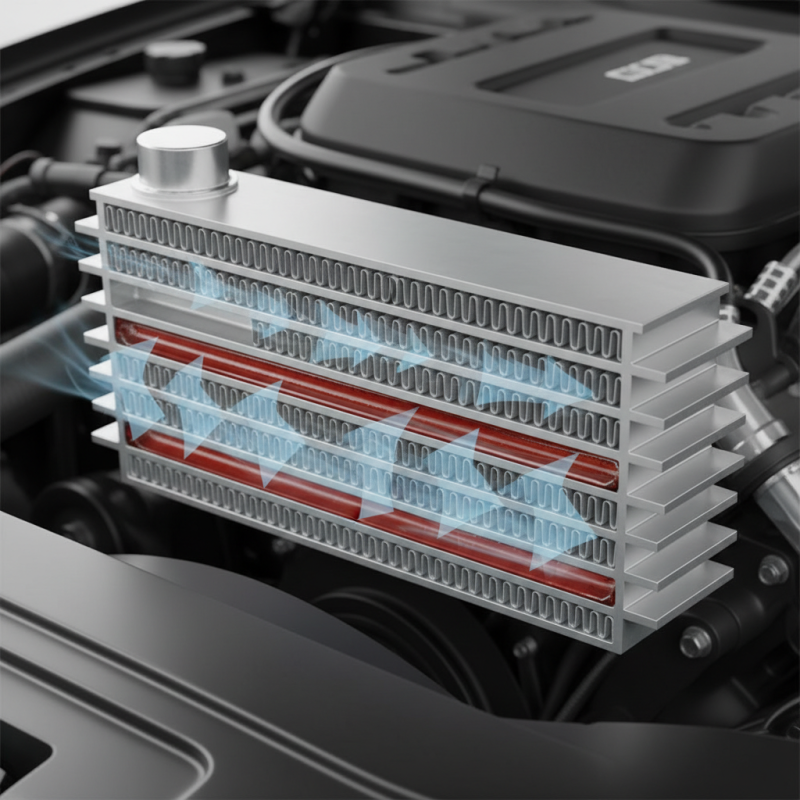
An air-cooled oil cooler is a device designed to lower the temperature of engine oil or transmission fluid through air convection. It plays a critical role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, especially in high-performance vehicles or heavy machinery where overheating can lead to decreased efficiency and potential damage. The core of an air-cooled oil cooler consists of a series of tubes or plates that allow the hot oil to flow through while ambient air circulates around them, drawing heat away from the oil.
The operation of an air-cooled oil cooler is relatively straightforward. As the hot oil enters the cooler, it passes through the internal channels where it is exposed to the cooler air outside. The heat from the oil is transferred to the air, which then leaves the cooler, allowing the oil to exit at a significantly lower temperature. This continuous cycle helps regulate oil temperature, ensuring proper lubrication and the prevention of oil breakdown. The design of air-cooled oil coolers can vary, but the fundamental principle remains the same: efficient heat exchange between the oil and air to enhance overall engine performance and longevity.
This chart compares the temperature reduction efficiency of different air cooled oil coolers under various engine load conditions. The data reflects the average temperature reduction achieved by these coolers during operation.
Air cooled oil coolers play a critical role in regulating the temperature of engine oil, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and lifespan of engines. The principle of operation for these coolers relies on ambient air to dissipate unwanted heat from the oil. When oil is circulated through the cooler, it passes through a series of finned tubes, which maximize surface area. Ambient air flows over these fins, drawing heat away from the oil via convection. According to industry reports, these coolers can reduce oil temperatures by up to 30% under typical operating conditions, significantly improving lubricant performance and engine durability.
The design of air cooled oil coolers varies, with some units featuring multiple passes to enhance heat exchange. The effectiveness of these coolers is influenced by factors such as air velocity, ambient temperature, and oil flow rate. A study published by the Society of Automotive Engineers highlights that optimizing these variables can result in thermal efficiencies exceeding 80%.
Furthermore, manufacturers are increasingly integrating advanced materials and designs that not only improve cooling performance but also contribute to a reduction in weight, making modern engines more efficient overall. This efficiency is crucial in industries where engine performance directly impacts productivity and operational costs.
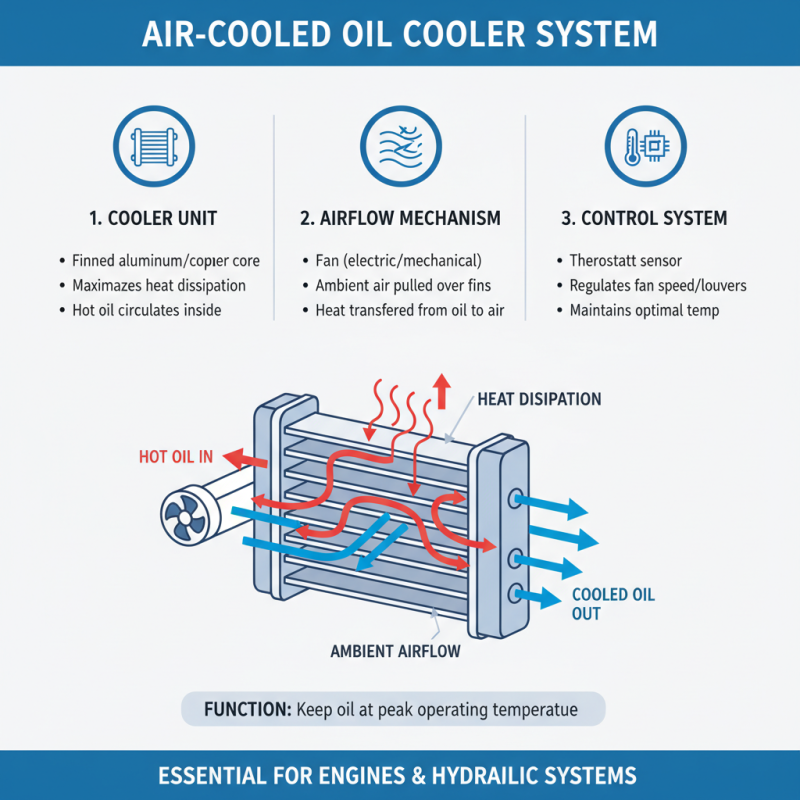
Air cooled oil coolers are essential components in many engines and hydraulic systems, designed to maintain optimal oil temperatures for efficient performance. The primary components of an air cooled oil cooler system include the cooler itself, air flow mechanisms, and a control system. The cooler typically consists of a series of aluminum or copper fins that maximize surface area for heat dissipation. As hot oil circulates through these fins, ambient air passes over them, allowing heat transfer away from the oil.
The air flow mechanism often employs a fan to enhance cooling efficiency, particularly in high-demand environments. Reports indicate that the efficiency of air cooled oil coolers can be significantly improved with the integration of variable speed fans that adjust based on oil temperature, providing better thermal management without wasting energy. Moreover, incorporating thermostatic controls ensures that the oil maintains an ideal temperature, preventing excessive wear and tear on engine components.
Tips: Regular maintenance of your air cooled oil cooler is crucial for its longevity. Clean the cooler's fins regularly to prevent dirt buildup, which can drastically reduce its efficiency. Additionally, consider monitoring oil temperatures closely; optimal operational ranges tend to fall between 180°F to 220°F (82°C to 104°C) for most engines, helping to avoid overheating or excessive cooling.
Air cooled oil coolers play a pivotal role in ensuring optimal engine performance, especially in vehicles operating under extreme conditions. One of the primary benefits of utilizing these systems is enhanced engine efficiency. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), maintaining oil temperatures within an optimal range can lead to improved fuel economy by as much as 5-10%. This reduction in temperature is vital as it mitigates oil breakdown, prolonging the life of engine components and reducing the overall maintenance costs associated with oil changes and repairs.
In addition to cost efficiency, air cooled oil coolers contribute to better thermal management. As engines generate heat during operation, an effective cooling system can prevent overheating, which is a common cause of engine failure. A report from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) suggests that vehicles equipped with air cooled oil coolers experience a 15-20% decrease in the likelihood of heat-related failures. This not only enhances vehicle reliability but also improves safety for drivers and passengers.
Tip: Regularly check and maintain your air cooled oil cooler to ensure its optimal functioning. A clean and unobstructed cooler will significantly improve your vehicle’s performance. Moreover, consider using high-quality engine oil that can withstand high temperatures, as it synergizes well with the cooling system to maximize efficiency.
Air cooled oil coolers are essential components in various industries where maintaining optimal oil temperatures is crucial for performance and reliability. One common application is in automotive engines, where these coolers help prevent oil from overheating, ensuring sufficient lubrication and reducing the risk of component wear. According to a report from the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), properly cooled engine oil can improve overall efficiency by up to 15%, underscoring the importance of air cooled oil coolers in vehicular systems.
Another significant application can be found in industrial machinery, particularly in hydraulic systems. Air cooled oil coolers maintain hydraulic fluid at optimal temperatures, which can enhance system responsiveness and prolong equipment life. A study conducted by the Hydraulic Institute indicates that temperature control can potentially extend the life of hydraulic components by 40%, resulting in substantial cost savings in maintenance and downtime. Industries such as construction and manufacturing increasingly rely on air cooled oil coolers to ensure their machinery operates smoothly under heavy loads and extreme conditions, highlighting the critical role these cooling systems play in industrial productivity.






